Fetal Medicine
Advanced fetal echocardiography for a detailed assessment of the baby's heart.
Advanced fetal echocardiography for a detailed assessment of the baby's heart.
Fetal Echocardiography (Fetal Echo) is a specialized ultrasound technique used to examine the structure and function of a baby’s heart before birth. It helps detect congenital heart defects and assess fetal heart development.
Who Needs It?
- Expecting mothers with a family history of congenital heart disease.
- Women with diabetes, lupus, or other high-risk conditions during pregnancy.
- Cases where an abnormal heartbeat or heart structure is detected in a routine ultrasound.
- Pregnancies resulting from IVF or multiple gestations.
Why is it Important?
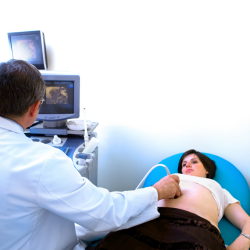
Uses of Fetal Medicine
Early Diagnosis of Fetal Conditions
Helps detect congenital abnormalities, genetic disorders, and developmental issues in the fetus.
Monitoring High-Risk Pregnancies
Provides specialized care for mothers with pre-existing conditions, multiple pregnancies, or complications.
Guidance for Medical Interventions
Assists in planning fetal surgeries, in-utero treatments, or post-birth medical procedures for better outcomes.
Preparation for Fetal Medicine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a fetal echocardiography test?
Fetal echocardiography is an ultrasound test that evaluates a baby’s heart structure and function while in the womb.
Why is fetal echocardiography done?
It is performed to detect congenital heart defects, monitor fetal heart function, and assess blood flow patterns, especially in high-risk pregnancies.
When is the best time to get a fetal echo test?
The test is usually done between 18-24 weeks of pregnancy when the fetal heart is developed enough for detailed imaging.
Is fetal echocardiography safe?
The radiologist will analyze the images, and your doctor will discuss the results with you, usually within a few hours or a day .
